Understanding the Tevo Tarantula CoreXY Conversion
Converting a Tevo Tarantula to a CoreXY configuration is a popular and rewarding upgrade for 3D printing enthusiasts. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough, detailing every step from gathering parts to achieving high-quality prints. The Tevo Tarantula, in its original Cartesian form, is a capable 3D printer. However, the CoreXY configuration offers several advantages that can significantly improve print quality, speed, and overall performance. This guide will help you understand why you’d want to undertake this conversion and what it entails.
Why Convert to CoreXY
The CoreXY design fundamentally alters the motion system of your 3D printer. Instead of the print head being driven directly by separate X and Y axis motors, CoreXY printers utilize a system of belts and two motors to control the movement of the print head in both the X and Y directions. This design choice leads to several performance benefits, making it a compelling upgrade for anyone looking to enhance their 3D printing experience. The main advantage of CoreXY is the potential for higher print speeds and improved print quality due to the reduced moving mass of the print head.
Benefits of CoreXY over Cartesian

CoreXY printers excel due to their inherent mechanical advantages. The print head, being lighter, can change direction much faster, leading to quicker print times. The symmetrical design of the CoreXY system also contributes to more consistent print quality, especially at higher speeds. Furthermore, the design often allows for a larger build volume within the same physical footprint, maximizing the printing area available. The CoreXY system also can reduce the ghosting effect compared to Cartesian systems. These aspects make CoreXY an attractive alternative for various 3D printing projects.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While CoreXY offers significant advantages, there are also factors to consider. The conversion process requires more advanced mechanical skills and a deeper understanding of 3D printer mechanics. The CoreXY system can be more complex to assemble and calibrate, requiring careful attention to detail during belt tensioning and alignment. The increased complexity might also introduce more points of failure. You’ll need to be prepared for a greater investment in time and potentially some troubleshooting. However, the improved print quality and speed gains often make the conversion a worthwhile endeavor.
Gathering Your Tevo Tarantula CoreXY Parts
Before starting the conversion, gathering the right parts is critical for a successful outcome. You’ll need a mix of replacement components, such as a CoreXY frame, belts, pulleys, and potentially upgraded motors or a new control board to handle the new configuration. This section details all the components you’ll need to acquire and recommendations for where to source them. A well-planned parts acquisition phase minimizes delays and ensures the build process goes smoothly.
Essential Components for the Conversion
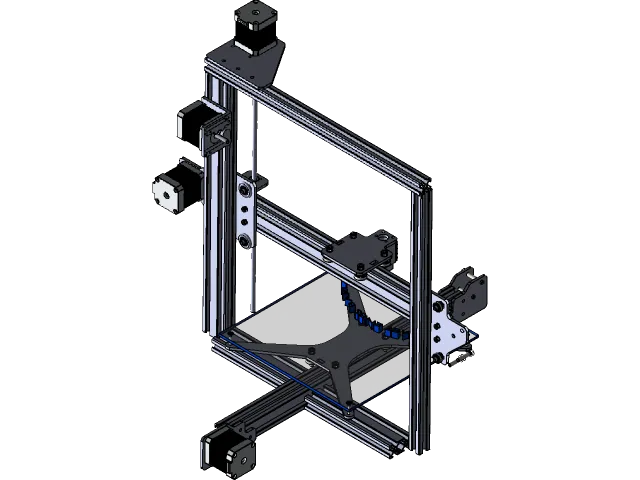
The essential components are what make the CoreXY system function. These include items like the CoreXY frame itself, which is often fabricated from aluminum extrusions to ensure rigidity. You’ll need quality GT2 belts and pulleys, chosen for their reliability and precision, and stepper motors. Also, consider whether your existing electronics, such as the mainboard, are compatible with the CoreXY configuration or whether an upgrade is needed. Properly selecting and sourcing these components is paramount. Furthermore, depending on the specific CoreXY conversion kit or design, other parts might be necessary.
CoreXY Frame Components
The frame is the backbone of your 3D printer and a crucial part of the CoreXY conversion. Several options exist, including purchasing a pre-designed CoreXY frame kit specifically for the Tevo Tarantula or designing and 3D printing your own customized frame components. If purchasing a kit, ensure it is compatible with your existing components (e.g., bed, heated bed, etc.) and offers the desired build volume. If you choose to design your own frame, consider using CAD software and aluminum extrusion. This allows for a high level of customization and optimization of the design.
Electronics and Control
The electronics system controls the motors and allows for communication with the CoreXY 3D printer. Ensure your existing mainboard can support CoreXY motion control, which is often the case with modern boards. If an upgrade is needed, consider options like the SKR Mini E3 series or similar boards, known for their excellent performance and ease of configuration. Research the firmware that will best fit your printer, as you will need to reflash the firmware to incorporate the CoreXY configuration and adjust settings to match the new components. Additionally, assess whether your power supply has enough capacity to power all the upgraded components.
Tools You’ll Need

Having the right tools will streamline the assembly process. A set of Allen wrenches or hex keys is essential for most 3D printers. A good quality screwdriver set is also necessary for various screws. A digital caliper ensures accurate measurements and alignment, which is critical for CoreXY builds. You may need wire strippers and crimpers for wiring, and a soldering iron may be useful. Having these tools prepared will allow for an easy, seamless build.
Step-by-Step Tevo Tarantula CoreXY Assembly Guide
With the necessary components and tools at hand, you are ready to begin the assembly. This section provides a detailed, step-by-step guide to converting your Tevo Tarantula to a CoreXY configuration. Following these steps carefully will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure a successful build. This process does require patience and attention to detail. Make sure to test each step as you go to avoid any issues later.
Disassembling the Original Tevo Tarantula
The first step in the conversion process involves disassembling the original Tevo Tarantula. This entails carefully removing all the components of the original Cartesian system. Label and organize all the screws and parts as you go. You will likely be reusing some components, such as the heated bed, so keeping track of everything is essential. Take pictures of the printer before disassembling it to help you remember how things were connected. This will be useful during the reassembly phase, making sure the new parts are arranged properly.
Removing Existing Components
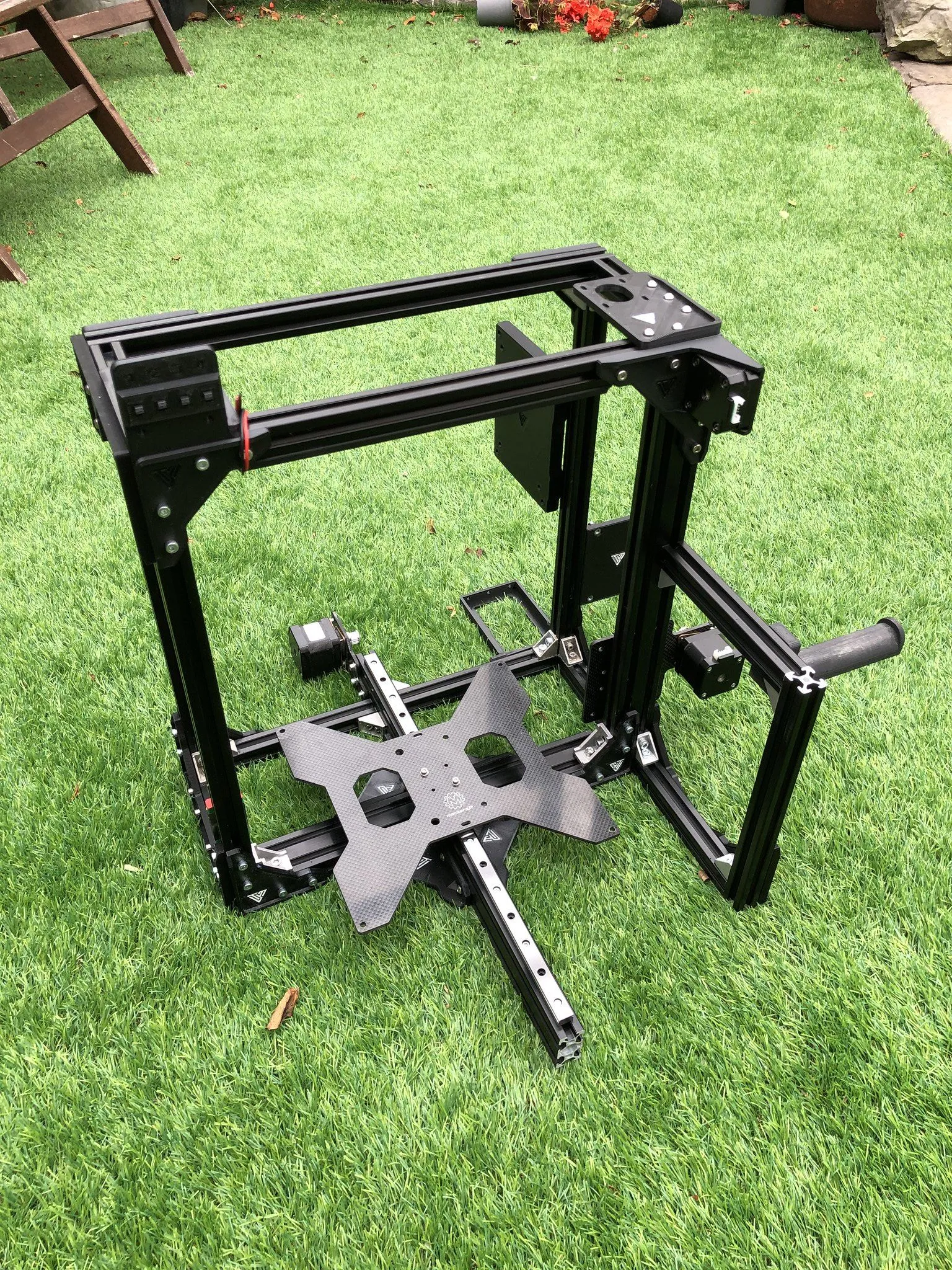

Start by disconnecting the power supply and removing all of the external connections. Then, carefully detach the X and Y axis motors, endstops, and print head. Remove the hot end, the print bed, and any other components that are attached to the existing frame. Disconnect all the wiring from the mainboard. Once you’ve removed these components, you should be left with the bare frame of the Tevo Tarantula, ready for the CoreXY conversion. Save all of the original parts in case you want to revert the printer to its original configuration.
Preparing the Frame for CoreXY
Once the original components are removed, prepare the frame for the new CoreXY components. This may involve drilling new holes or modifying existing ones, depending on the design. Ensure the frame is square and level to prevent any printing issues down the line. If using a pre-made kit, follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. If designing your own frame, measure twice and cut once to ensure everything fits properly. Properly preparing the frame guarantees a solid and stable base for the CoreXY motion system.
Installing the CoreXY Motion System
This is the core of the conversion. The CoreXY motion system involves installing the two stepper motors, the belts, and the pulleys in the new configuration. The X and Y axes are now controlled by the two motors working in tandem. This often involves attaching the motors to the frame, routing the belts through the pulleys, and mounting the print head carriage. Follow the kit instructions precisely and double-check all the alignments to avoid problems. Correctly installing the motion system is critical for ensuring that your printer can move smoothly and accurately.
Belt Routing and Tensioning

Proper belt routing and tensioning is vital for print quality and reliability. Belts that are too loose will cause print inaccuracies, while belts that are too tight can damage the motors or pulleys. The belts in a CoreXY system must follow a specific path to ensure the print head moves correctly in the X and Y directions. Pay close attention to the diagram, and make sure the belts run parallel to each other and the frame. Once routed, tension the belts according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Test by gently pushing the print head; there should be minimal give in the belts.
Wiring and Electronics Setup
After installing the mechanical components, the next step is wiring the electronics. Reconnect the stepper motor wires to the mainboard. The wiring configuration might be different from the original Cartesian setup. Follow the wiring diagram provided with the CoreXY kit or your new mainboard. Connect the endstops, the hot end, the heated bed, and any other peripherals. Ensure all connections are secure to avoid short circuits or other problems. Carefully check the wiring to avoid any mistakes, as this is key to keeping your printer functional and preventing any safety issues.
Configuring Firmware for CoreXY
The final step in the assembly phase is configuring the firmware. Download the appropriate firmware (Marlin is a popular choice) and configure it for a CoreXY printer. This includes setting the correct steps per millimeter, the motor direction, and the endstop positions. You may need to calibrate the PID settings for the hot end and bed. Update your settings using software and verify that all of your changes have been saved. You will also have to configure the firmware for the correct print bed size. Once this step is done, your printer is ready to be tested.
Testing and Calibration
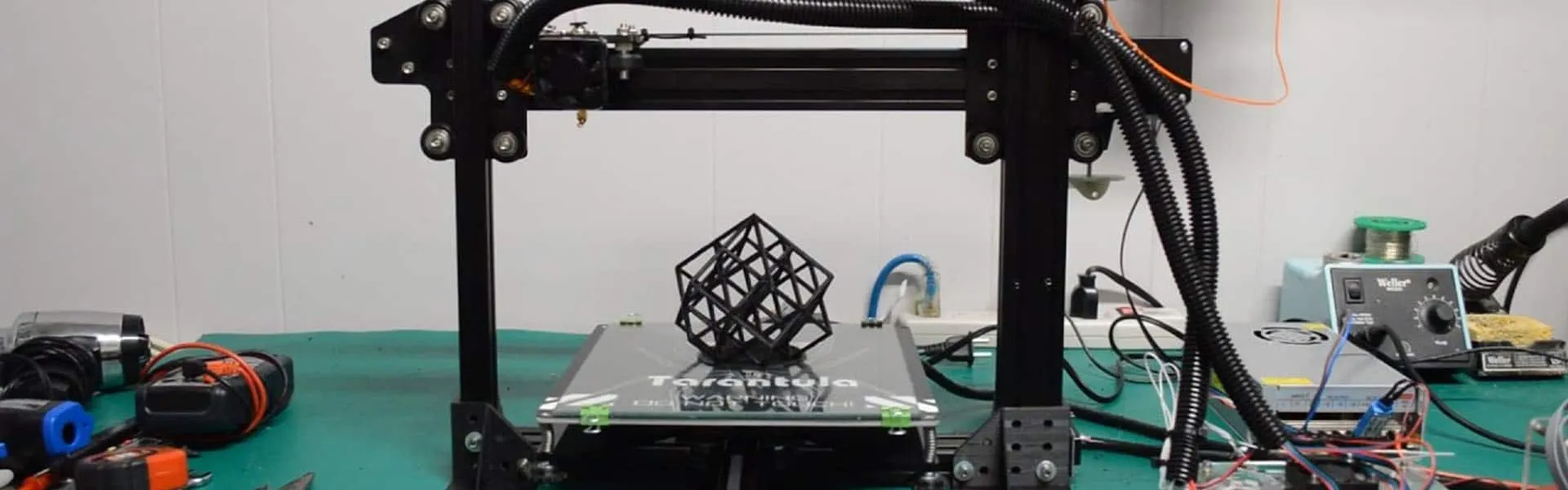
Once the assembly is complete and the firmware is configured, the next step involves testing and calibrating your new CoreXY printer. This process ensures everything works correctly and that you are getting high-quality prints. Take your time with calibration, as this can greatly affect the final print results. Print some test prints and watch for any errors or issues.
Bed Leveling and Calibration
Leveling the print bed is one of the most critical calibration steps. A properly leveled bed ensures that the first layer of your print adheres correctly. Use the bed leveling procedure recommended by your firmware or printer kit. Often, this involves adjusting the bed height using leveling screws while the printer homes. Once the bed is leveled, you can calibrate the Z-offset. This is the distance between the nozzle and the bed during the first layer. Calibrate carefully to ensure proper bed adhesion.
First Print and Fine-Tuning
Once the printer is assembled, the bed is leveled, and you’ve calibrated your Z-offset, it’s time to make your first print. Start with a simple test print, such as a calibration cube. This will let you check the overall dimensions of the print and identify any potential issues. Examine the layers of the print for any inconsistencies. Fine-tune your printer by adjusting the bed temperature, print speed, and retraction settings. Experiment to find the optimal settings for different filament types. Be sure to monitor your first few prints carefully and make the necessary adjustments to improve print quality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Even with careful assembly and calibration, you may encounter some issues. This section covers the most common problems and provides solutions. Having some troubleshooting strategies available will allow you to quickly identify and fix any problems. Patience and a willingness to experiment are key to resolving any issues.
Belt Slippage and Tension Problems
Belt slippage can result in print inaccuracies, such as layers that are not aligned correctly. Ensure that the belts are properly tensioned. If the belts are slipping, try tightening them slightly. Check the pulleys and make sure they are securely fastened to the motor shafts. Also, check the grub screws on the pulleys to ensure they are tight against the motor shafts. In extreme cases, you might need to replace the belts or pulleys. Check for any obstructions along the belt path and remove them. Finally, reduce the acceleration and jerk settings in your firmware to minimize the stress on the belts.
Print Quality Issues and Solutions
Several print quality issues might arise. Layer shifting is a common problem caused by loose belts, incorrect motor currents, or obstructions in the motion system. Ensure that the belts are properly tensioned and the frame is stable. Over-extrusion or under-extrusion can impact print quality. Adjust the flow rate in your slicer or calibrate your extruder. Wobbling or ringing can be caused by vibrations. Reduce the print speed or tighten the frame components. Make sure your bed is level and your first layer is properly adhered. Experiment with different slicer settings to optimize print quality.
Software and Slicing Settings for CoreXY
Proper slicing settings are crucial for achieving high-quality prints with a CoreXY printer. Adjusting the settings for the CoreXY system will optimize the speed and print quality. Cura, PrusaSlicer, and Simplify3D are all popular slicing programs. Make sure to select the correct printer profile that matches your configuration. The settings that you adjust in the slicer will make sure your printer is correctly calibrated. Start with a low print speed and gradually increase it until you achieve a balance between speed and quality. Optimize the acceleration and jerk settings. Experiment with different filament types to determine the best settings for your setup.
